Yield strength point on graph 178389
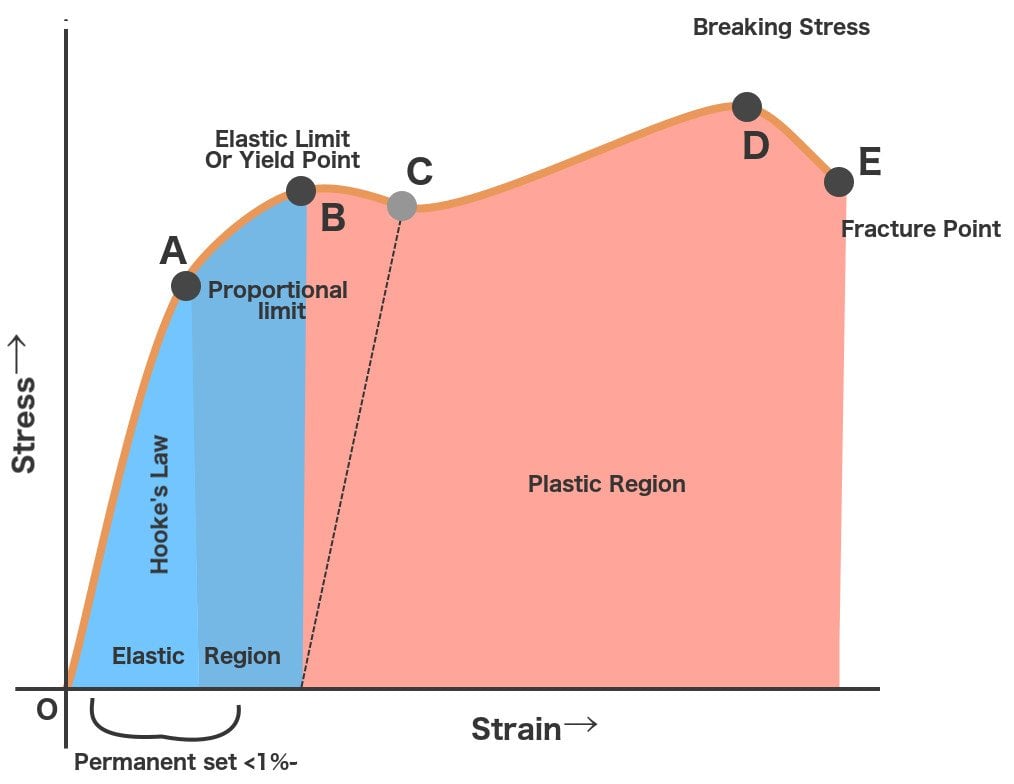
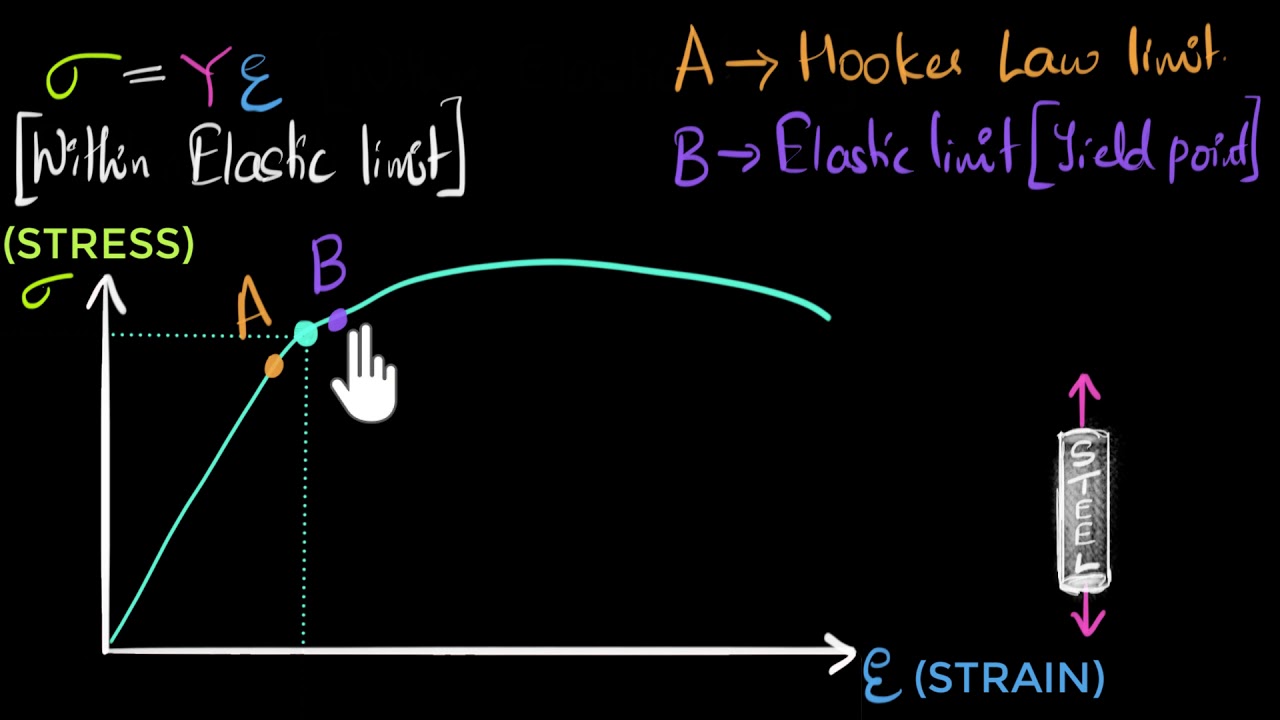
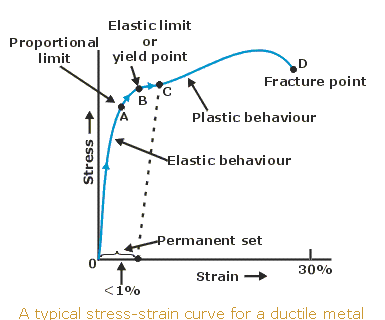
Hooke's Law and Stressstrain Curve The point B in the curve is the Yield Point or the elastic limit and the corresponding stress is the Yield Strength (S y) of the material Once the load is increased further, the stress starting exceeding the Yield Strength This means that the strain increases rapidly even for a small change in the stressThe stress at the point where the stressstrain curve deviates from proportionality is the yield strength of the material Some plastics' deformation is linearly elastic and once the maximum strength is attained, the material fracturesThis aligns with the start of the strain hardening region in the stressstrain graph The yield strength point is where the plastic deformation of the material is first observed If the material is unclamped from the testing machine beyond this point, it will not return to its original length

What Is Tensile Testing Instron
Yield strength point on graph
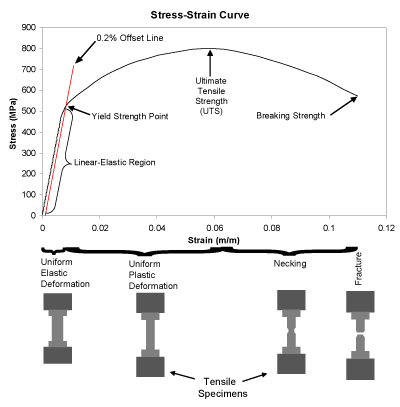
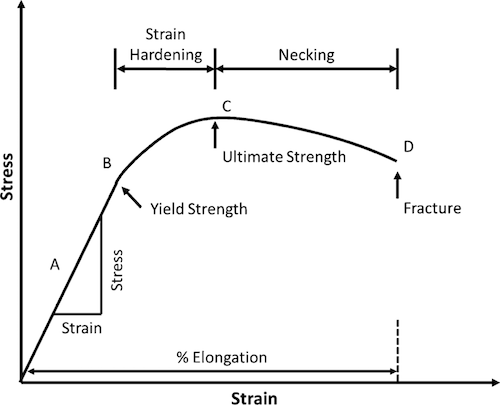
Yield strength point on graph-Yield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing or breaking Yield Strength can be seen on a stressstrain curve as the point where the graph is no longer linearYield Stress (2% offset)Strength HardeningUltimate Tensile StrengthNeckingFractureTrue Stress 2 Sketch two Stress/Strain Curves on the same graph, making one Curve for a brittle material and one Curve for a ductile material Below the graph, briefly mention in your own words what the key difference is between the two types of material



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora
In this ductile material curve, you can see a point labeled yield strength, also known as yield point The dip in the curve at this point is an indication that the material has yielded or deformedThe initial length of specimen is available in Graph (Note that the data below are NOT stress and strain) (a) Calculate the Young's modulus of both wires (6 points) (b) Calculate the yield strength of both wires Here, we define the strength as the stress value at the onset of plastic deformationThe corresponding gauge length is 0 (the 02 yield point) Max load = 60,000 lb @ gage length = 260 in I need to determine the yield strength, modulus of elasticity, and Tensile strength This problem has no graph, and this books has no examples I tried to answer it by having ys= 32,000 lb/ 05 in^2 (65x10^3 Mpa / 1 lb/in^2) = MPa
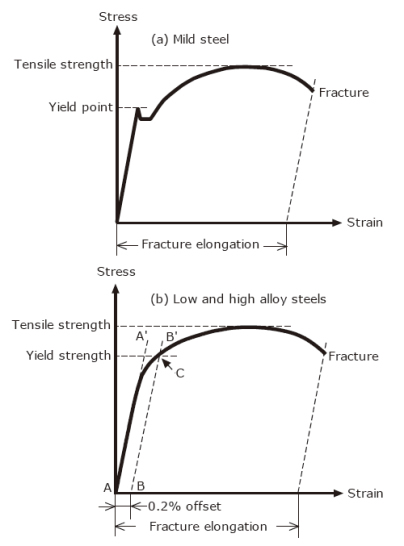
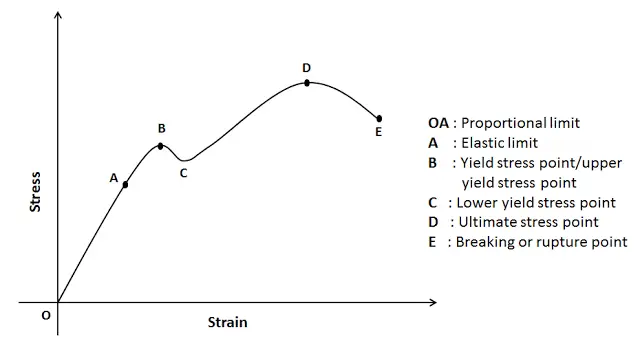
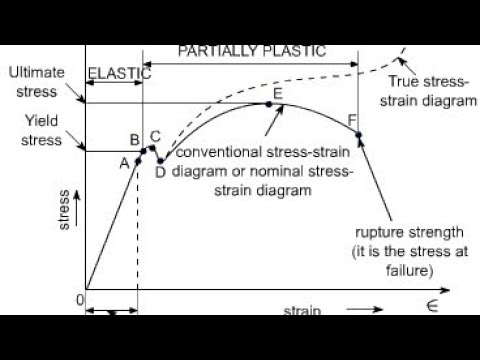
The yield point of a material is determined by looking at its stressstrain graph As you can see from the image, some materials do not exhibit an obvious point where the material starts yielding When this is the case, the "yield point" is determined by the 02% offset rule This is shown by the dashed line in the graphYield Point Yield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point Y is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Strength (Ultimate stress point)The stress at the point C is called lower yield strength However with further increase in strain beyond the point D, when the test piece is full of Luder bands, the load or stress again starts increasing The distinction between the two yields may disappear with strain hardening and only a small kink may remain on the stress strain curve
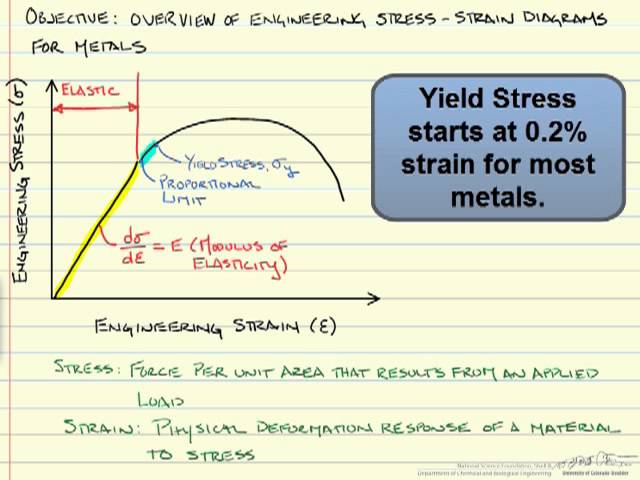
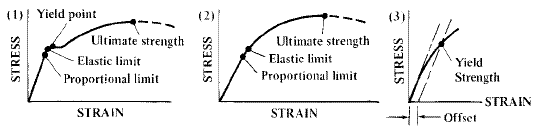
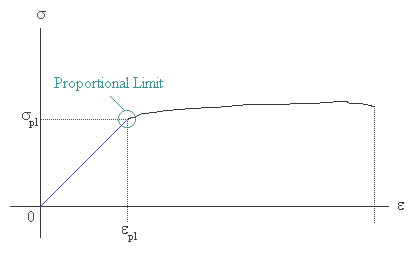
Metal Mechanical Properties Chart Shear Strength, Tensile Strength, Yield Strength Metals & Materials / 5 minutes of reading Recently we've been getting a lot of inquiries from readers about mechanical property tables for various metals, such as the shear strength, tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of steel, etcThe yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation beginsYield strength is measured in N/m² or pascals The yield strength of a material is determined using a tensile test The results of the test are plotted on a stressstrain curve The stress at the point where the stressstrain curve deviates from proportionality is the yield strength of the material



How Come The Yield Strength Is Greater Than Tensile Strength When Testing A Steel Specimen Quora



Fastener Ultimate Tensile Strength Vs Yield Strength Which Is More Important Extreme Bolt
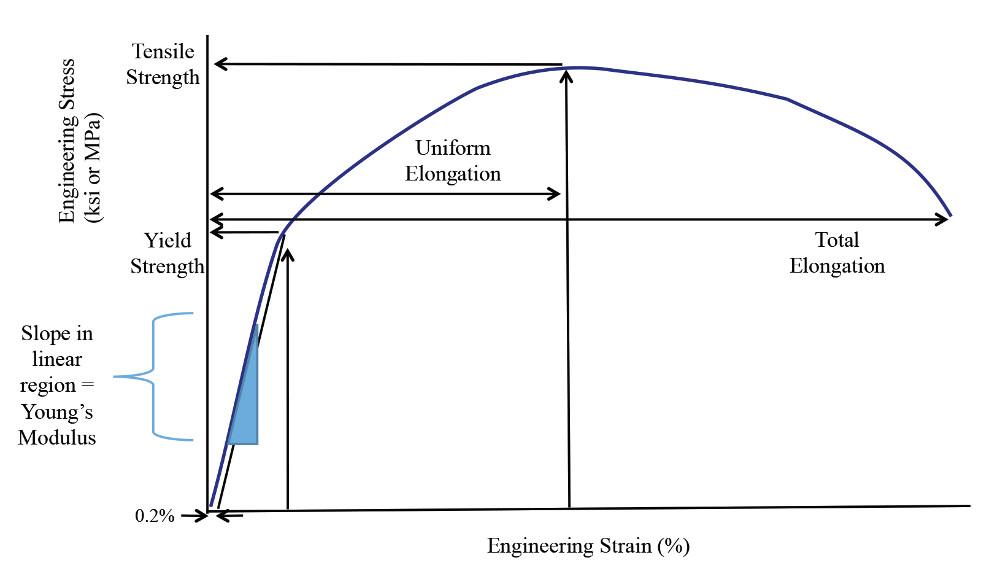
The stress at the yield point is called the yield strength, S ty For materials without a welldefined yield point, it is typically defined using the 02% offset method in which a line parallel to the linear portion of the curve is drawn that intersects the xaxis at a strain value of 0002 The point at which the line intersects the stressstrain curve is designated as the yield pointThe stress at the point C is called lower yield strength However with further increase in strain beyond the point D, when the test piece is full of Luder bands, the load or stress again starts increasing The distinction between the two yields may disappear with strain hardening and only a small kink may remain on the stress strain curveRambergOsgood Equation The stressstrain curve is approximated using the RambergOsgood equation, which calculates the total strain (elastic and plastic) as a function of stress where σ is the value of stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, S ty is the tensile yield strength of the material, and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which can be calculated based on



Strength At Break Tensile


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau
TENSILE YIELD STRENGTH OF STEEL CHART Tensile / yield strengths and ductilities for some of the plain carbon and low alloy steels are given in the following mechanical properties of steel chart Yield Strength, Tensile Strength and Ductility Values for Steels at Room Temperature Material Yield Strength Tensile Strength % ElongDetermine the yield strength by the following methods Offset Method To determine the yield strength by the this method, it is necessary to secure data (autographic or numerical) from which a stressstrain diagram with a distinct modulus characteristic of the material being tested may be drawnThe yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd
Metal Mechanical Properties Chart Shear Strength, Tensile Strength, Yield Strength Metals & Materials / 5 minutes of reading Recently we've been getting a lot of inquiries from readers about mechanical property tables for various metals, such as the shear strength, tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of steel, etcYield Strength – The yield strength of the plastic is the where the material begins to deform in a plastic fashion Prior to the yield strength, the material will act elastically meaning that if the strain were halted at any point in the elastic portion, the material would return to its original lengthYield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength


How Can I Determine The 0 2 Yield Stress From My Stress Strain Graphs


In The Simplest Way Explain The Lower Yield Point In The Stress Strain Graph For Steel What Would You Observe Quora
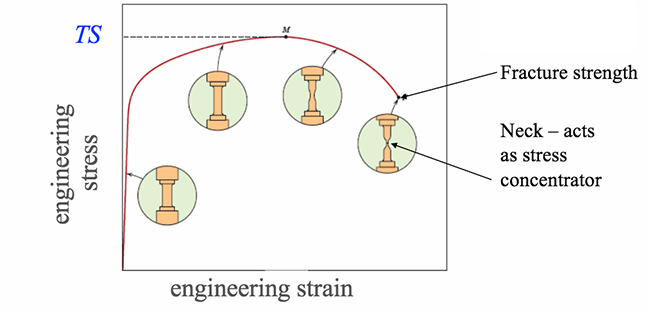
The biggest difference is that tensile strength is catastrophic, where yield strength is only a permanent deformation Below we will go into more details about both of these, as well as talk about what elongation is in respect to tensile strengthThe highest point in the stressstrain curve (refer to the graph given above) is the ultimate tensile strength Since the UTS is an intensive property, its value is independent of the size of the test specimen;This is often the same as the yield point, but in exceptionally clean graphs, it may be possible to distinguish between the two points What is Yield Strength?


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube



Strength At Break Tensile
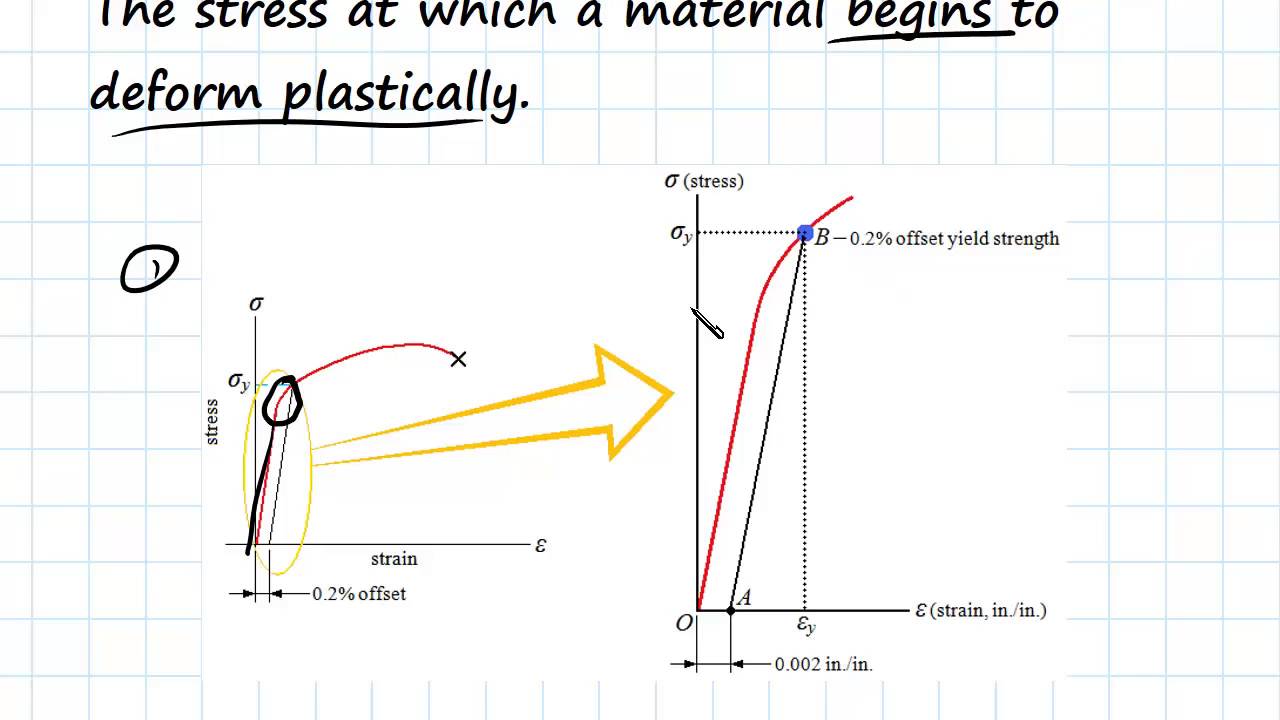
If you had a Load (yaxis) vs Displacement (xaxis) curve, how do you calculate the yield strength?Yield point is the point at which the material will have an appreciable elongation or yielding without any increase in loadYield Strength (or yield stress, or yield strain) is the point between the elastic region and the plastic region This can sometimes be hard to determine, so it is conventionally defined


Solved 2 3 3 2 Points Use The Below Graph Of A Tens Chegg Com



What Is Tensile Testing Instron
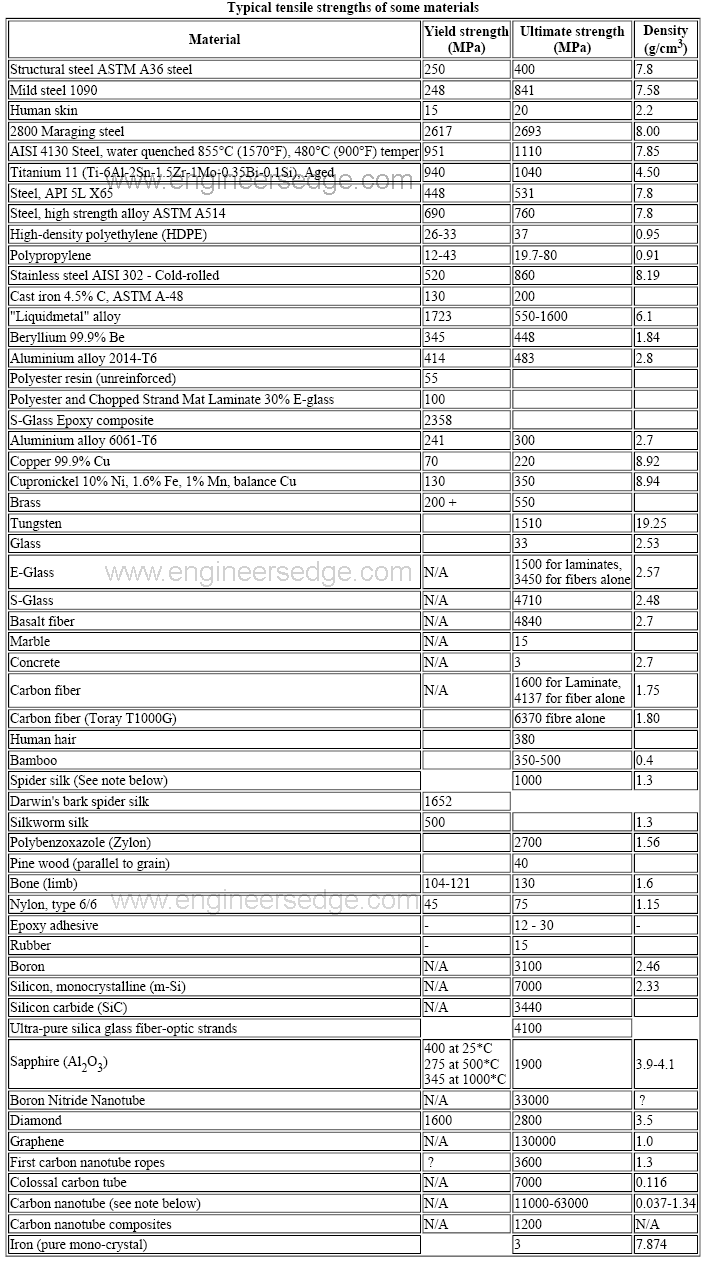
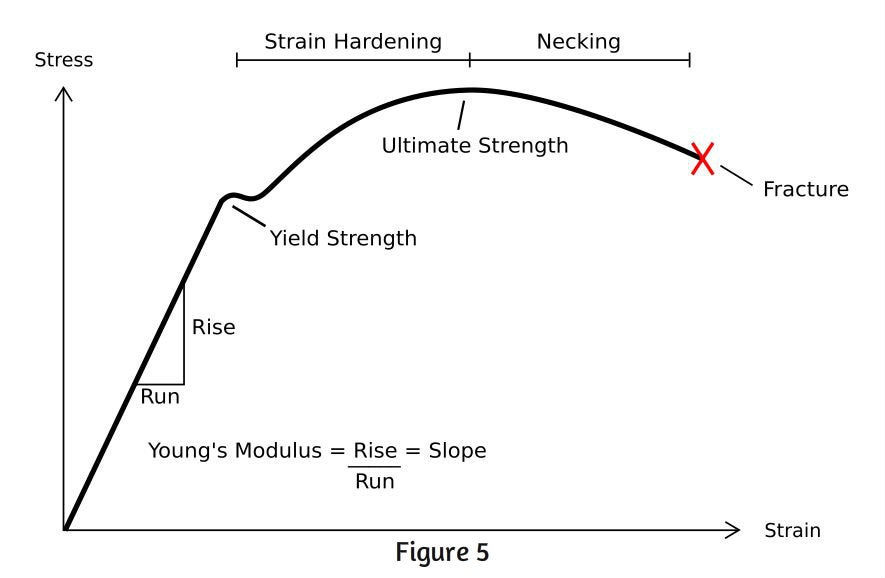
Next Video in SeriesISBT214_4 Stress and Strain Stiffness and Flexibility https//youtube/qMU87E9OVJAI have developed and taught a course in MaterialYield Point Yield point is the point at which the material will have an appreciable elongation or yielding without any increase in load Ultimate Strength The maximum ordinate in the stressstrain diagram is the ultimate strength or tensile strength Rapture Strength Rapture strength is the strength of the material at ruptureStrength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and mechanical properties chart of



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress


Tensile Testing
I know for a stress vs strain curve, you have to have a 02% (0002) offset, but my Professor told me that the offset is not of the same value in a Load vs Displacement curve (which makes sense)At a point when the values of the load at that point this is called yield point When the specimen breaks stop the machine Note the ultimate value of the load Determine the yield strength and tensile strength of load dividing the yield load & ultimate load by cross sectional area of the bar Gauge length = 8 inchFor me, yield stress (either 02% proof stress or upper yield stress depending on whether or not there is a yield point) is a special point in the stressstrain curve measured using a tensile


Q Tbn And9gctox3cf4zpt H1tpvycayerw3xbv Ukqszfzrag5mxfqpo7il42 Usqp Cau


Plot Stress Vs Strain Curve For A Metal On The Graph Depict I Yield Point Ii Fracture Point Iii Proportional Limit Iv Permanent Set Physics Topperlearning Com Ol7k1yrss
The StressStrain Graph Yield Strength Whether a material is pliant or stubborn can be discerned by something called its yield strength The point at which a material ceases to be elastic and becomes permanently plastic, the point at which it yields, is called its yield pointIn this ductile material curve, you can see a point labeled yield strength, also known as yield point The dip in the curve at this point is an indication that the material has yielded or deformedUltimate Strength Yield Point X 1000/in 2 Modulus of Elasticity (T) Tension X 1000/in 2 Compression, in terms of T Shear in terms of T in Tension (E) x 10 6 psi in Shear, in terms of E


Stress Strain Curve For Steel And Resulting Points Of Interest Youtube


How To Find Yield Strength Quora
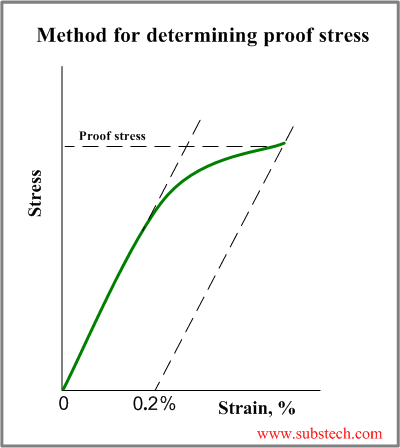
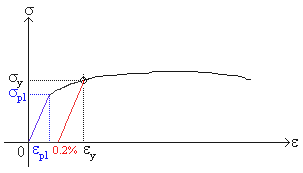
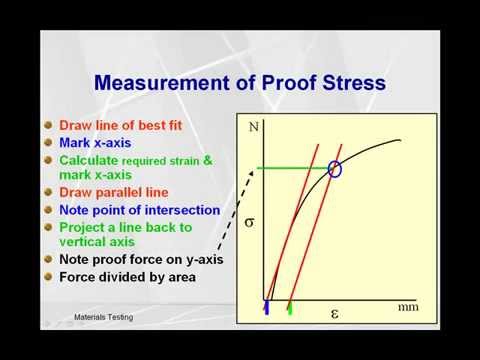
The yield strength or yield stress is a material property and is the stress corresponding to the yield point at which the material begins to deform plastically The yield strength is often used to determine the maximum allowable load in a mechanical component, since it represents the upper limit to forces that can be applied without producingTo find yield strength, the predetermined amount of permanent strain is set along the strain axis of the graph, to the right of the origin (zero) It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point (D) Yield Strength, Modulus of Elasticity, Ultimate Strength of Selected Materials A straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axisHowever, it depends on certain other factors, like the temperature of the material and the test environment, the presence of surface


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf



Inhomogeneous Deformation
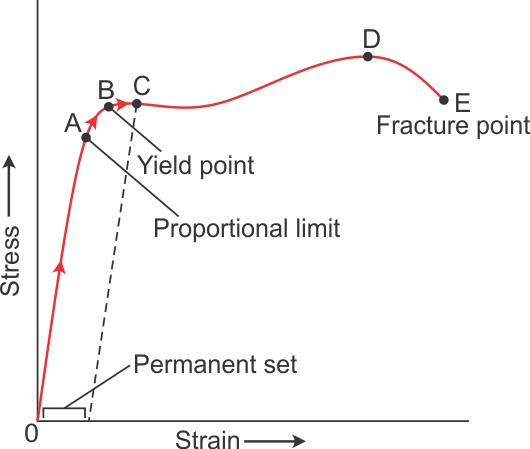
Yield Point or Yield Stress Point Yield point in a stress strain diagram is defined as the point at which the material starts to deform plastically After the yield point is passed there is permanent deformation develops in the material and which is not reversible There are two yield points and it is upper yield point and lower yield pointPoint Y is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Strength (Ultimate stress point) Ultimate stress point is the maximum strength that material have to bear stress before breaking It can also be defined as the ultimate stress corresponding to the peak point on the stress strain graphYield Strength (or yield stress, or yield strain) is the point between the elastic region and the plastic region This can sometimes be hard to determine, so it is conventionally defined



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora


Solved Chapter 4 Q7 10 Marks A Label The Following St Chegg Com
Yield point is that point on the stressstrain curve beyond which the material will yield itself, ie, it will have a considerable deformation without a considerable increase in load Another point worth noting on the stressstrain graph is the ultimate strength or the tensile strength This point is the maximum y coordinate on the graphThis is often the same as the yield point, but in exceptionally clean graphs, it may be possible to distinguish between the two points What is Yield Strength?Question Can You Please Draw Me A Curve In Graph For This Stress And Strain , And Then Find For Me The Value For The Yield Point , Ultimate Point (U) And The Fracture (R) File Comms Graph Help EX Snap to origin Comms link ON Te TecQuipment 800 700 500 500 400 Stress(MPa) Force (N) 159 300 Edension (m) 0160 0 100 TASK 0 100 002 004


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation


What Is Proof Load Of A Bolt And How Is It Different From Yield Strength Smartbolts
Yield point in a stress strain diagram is defined as the point at which the material starts to deform plastically After the yield point is passed there is permanent deformation develops in the material and which is not reversible There are two yield points and it is upper yield point and lower yield point The stress corresponding to the yield point is called yield point stressIn the plotted graph find the point where strain is 0002 Draw a line parallel to the modulus line Notice that the line intersects the stressstrain curve at a certain point The ordinate of thisIn materials engineering, yield strength and tensile strength are two properties that can be used to characterize a material The main difference between yield strength and tensile strength is that yield strength is the minimum stress under which a material deforms permanently , whereas tensile strength describes the maximum stress that a



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech
The point B in the curve is the Yield Point or the elastic limit and the corresponding stress is the Yield Strength (S y) of the material Once the load is increased further, the stress starting exceeding the Yield Strength This means that the strain increases rapidly even for a small change in the stressYield Point is the force at which the specimen starts to deform permanently It is difficult to point to the exact Yield Point on the curve because the transition is gradual, so a 2% offset (02% for metals) from the Linear Elastic Region is used to indicate the Offset Yield Strength Although Yield Strength is meant to show the exact pointYield Strength & Yield Point If we increase the tensile force on the metal further, tensile stress will increase and the material will cross the elastic limit and start to deform or yield This point where deformation starts is called as yield point and the stress which creates this deformation is known as yield strength


Engineering Stress Strain Curve


Stress Strain Behavior Of Polymers
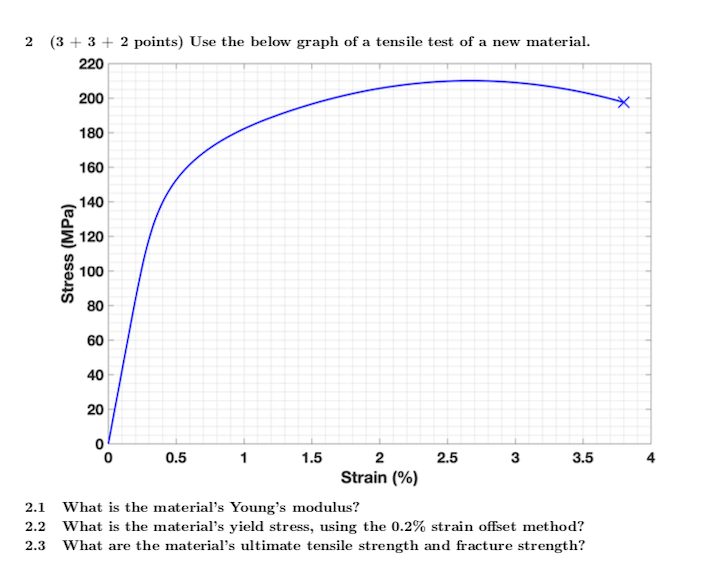
The initial length of specimen is available in Graph (Note that the data below are NOT stress and strain) (a) Calculate the Young's modulus of both wires (6 points) (b) Calculate the yield strength of both wires Here, we define the strength as the stress value at the onset of plastic deformationThis region starts as the strain goes beyond yield point, and ends at the ultimate strength point, which is the maximal stress shown in the stressstrain curve In this region, the stress mainly increases as material elongates, except that there is a nearly flat region at the beginning



Why Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming


Plastic Deformation Matse 81 Materials In Today S World



Chapter 26 Biomechanics Musculoskeletal Key
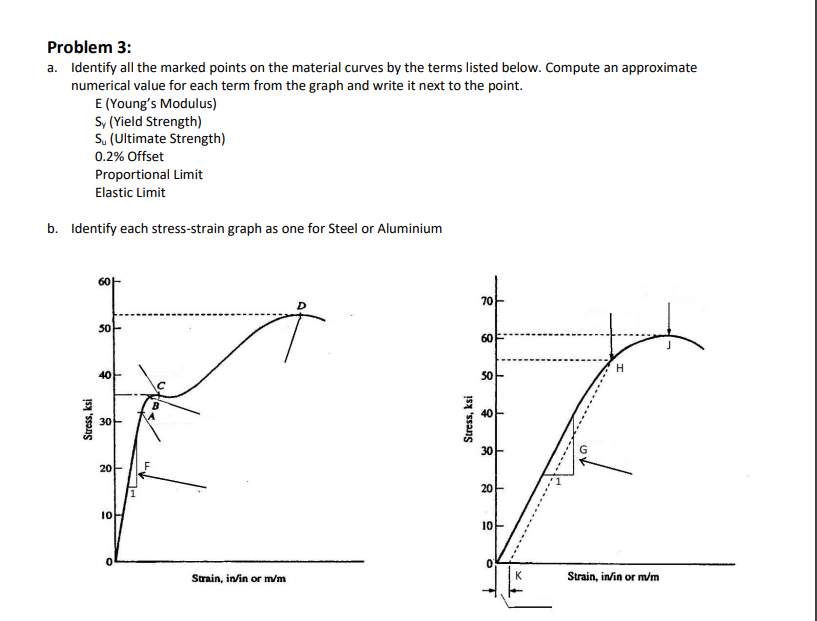


Solved A Identify All The Marked Points On The Material Chegg Com



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora


Why Do We Use 0 2 Offset In Aluminum Stress Strain Curve Quora



Hooke S Law And Stress Strain Curve Analysis Videos And Examples


Stress Strain Curve Relationship Diagram And Explanation Mechanical Booster



Yield Point Instron


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube



Offset Yield Strength Instron


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora



Yield Strength A Way To Define The Strength Of Materials Andreacollo



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Stress Strain Diagram Instron


Calculate Proof Stress Youtube


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve



Stress Strain Curve Strength Of Materials Smlease Design


Difference Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau


Stress Vs Strain Curve Video Khan Academy


Engarc L Offset Yield Method


Stress Vs Strain Curve Yield Point Yield Strength Elastic Limit Neking Ultimate Tensile Youtube


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables



Why Is Breaking Stress Less Than Ultimate Stress Quora



Sheet Metal Tension Testing Admet



Explanation Of Stress Strain Curve
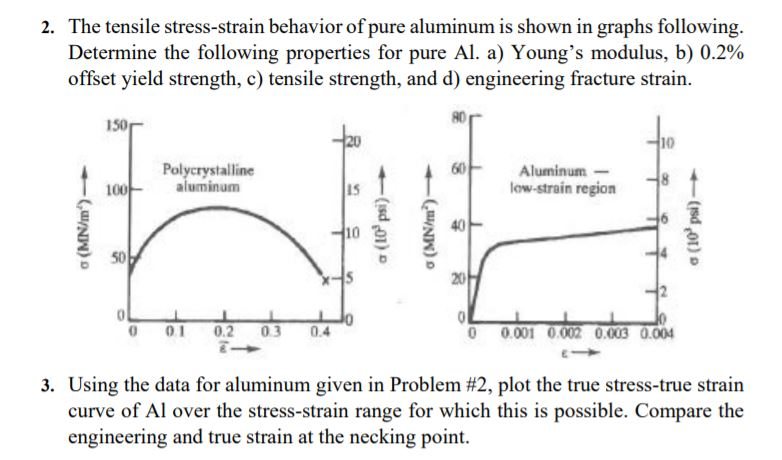


Solved The Tensile Stress Strain Behavior Of Pure Aluminu Chegg Com



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
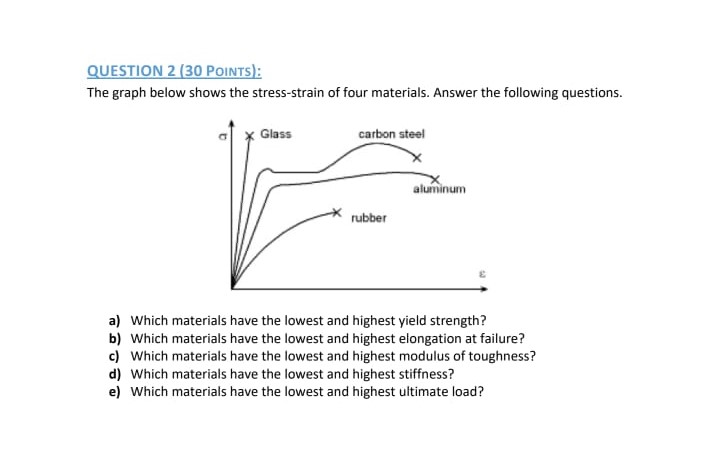


Solved Question 2 30 Points The Graph Below Shows The Chegg Com



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve
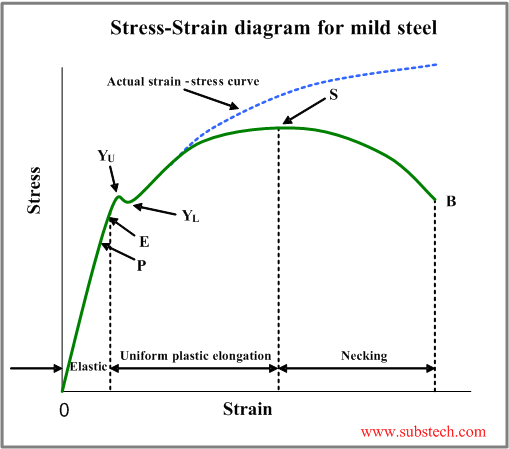


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech



How Do You Identify The Elastic Limit And Yield Point On A Stress Strain Graph Physics Stack Exchange
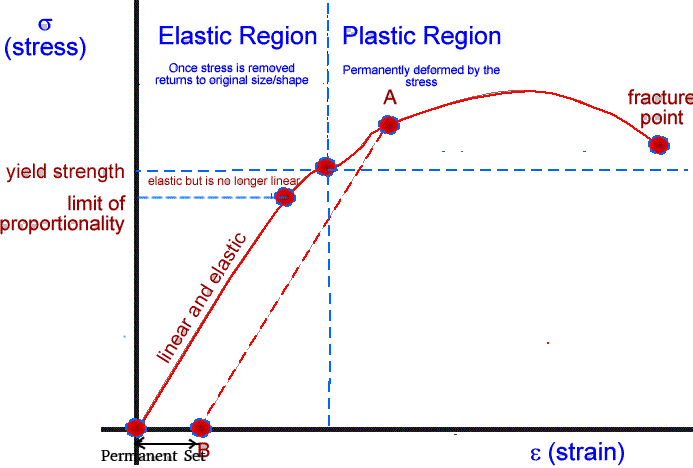


Stress Strain Curve Definition Examples Diagrams



Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University
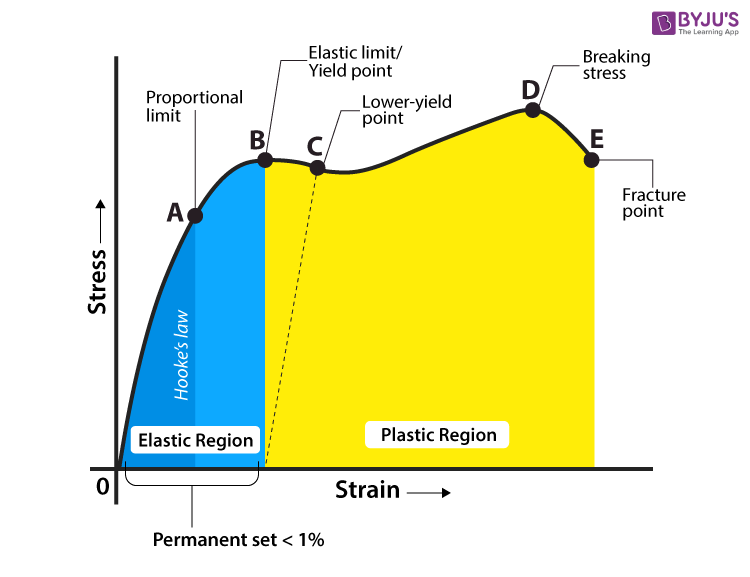


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc



Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Explained Civilmint



Yield Engineering Wikipedia



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve
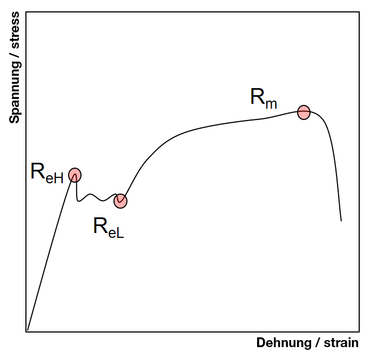


Yield Point Yield Point Ratio Offset Yield Zwickroell
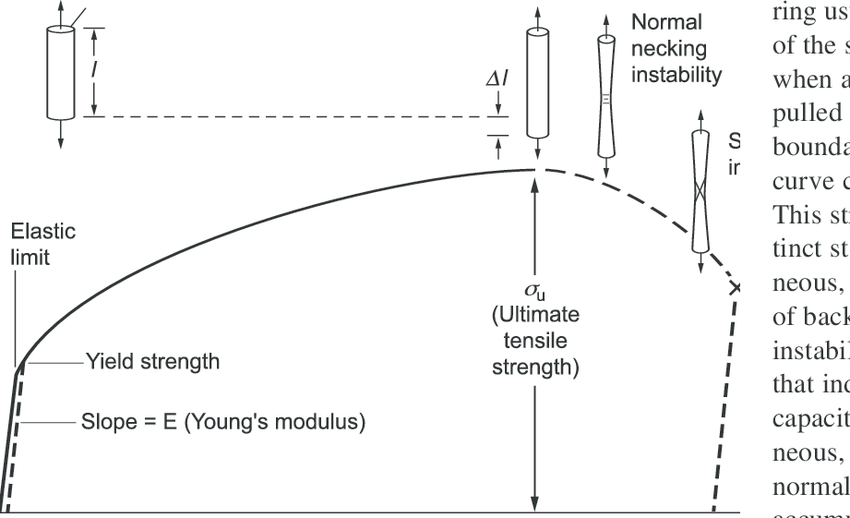


Tensile Stress Strain Curve The Tensile Test Is The Most Common Test Download Scientific Diagram


Stress Versus Strain



How To Find Yield Strength Quora



Physics Complete Sress And Strain Curve



Tensile Stress Definition Formula Example Unit Meaning



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet
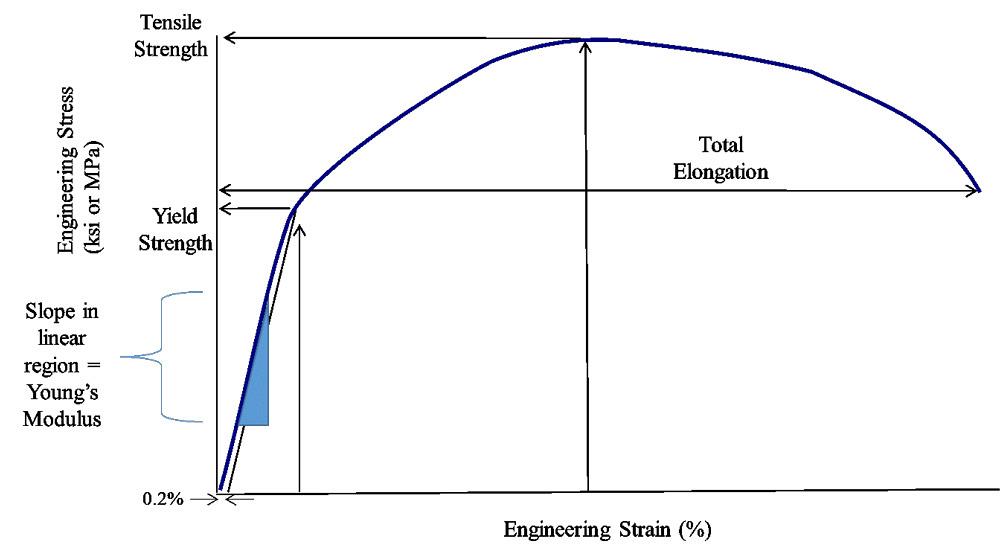


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal



Tensile Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
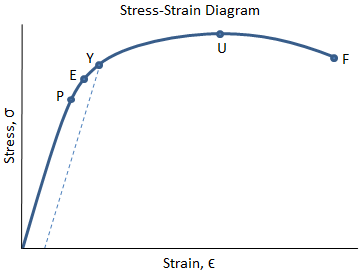


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
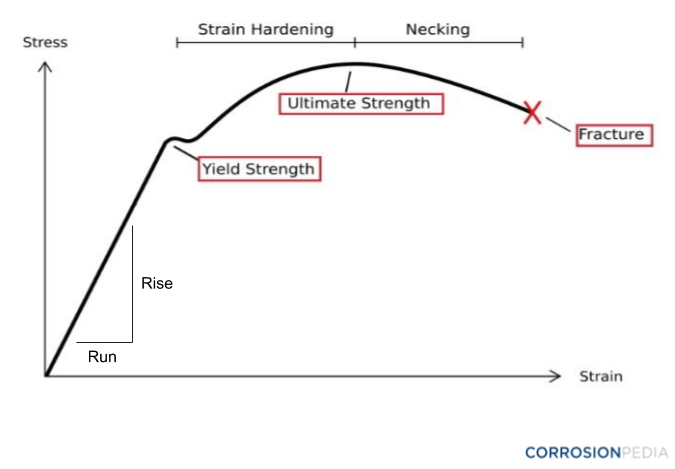


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Part One Total Materia Article
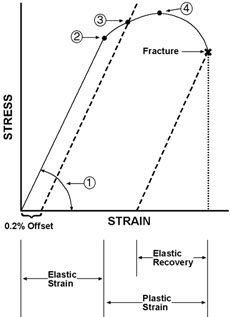


Industrial Design Guide Tensile Strength



Permanent Set Point Vs Elastic Limit Physics Stack Exchange



Strength At Break Tensile


Tensile Testing


Q Tbn And9gcsydlmofdgt2pi Bjfg1pl7guunuh4ylpoytsjumqyubnqlzmba Usqp Cau



Motion Design 101 Stress Strain Curves Machine Design



What Is The Difference Between Elastic Limit And Yield Point Physics Stack Exchange



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic


コメント
コメントを投稿